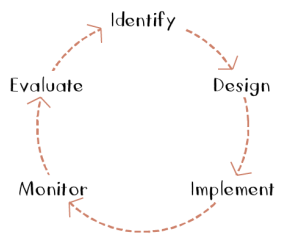
Identify
The situation has to be analysed and the target group needs to be identified. Careful project planning will include a context analysis and a needs assessment to make sure that there is an actual need for increased job opportunities, improved political participation or new forms of community engagement.
Design
In the design stage you will think about your objectives and how to obtain them.
This means already thinking about impact, outcomes and activities as well as the resources you have at your disposal and those you still need for the project to be realized.
Another aspect of the design is carrying out a risk assessment and do no harm analysis in order to avoid unintended results.
Implement
Projects have implementation phases of different lengths during which they carry out their activities, but you can also plan one activity at a time and then implement them.
This way you will have a greater control over adjusting the project in case something did not work as planned and the potential to apply lessons learned will be greater.
However, projects with a lower frequency of activities might struggle with lower efficacy.
Monitor
Monitoring occurs at all project stages and should give you information on whether your project is on track vis-à-vis its objectives or whether something needs adjustment.
It will be your responsibility to create indicators that reliably measure whether you are achieving your goals.
Evaluate
Evaluation is an immensely important part of the project, yet countless organization fail to allocate the needed resources of a project budget to the evaluation process of collecting, analyzing and interpreting data.
The evaluation tells whether objectives were reached, and points out the lessons to be learned from the project.
Especially when applying for funds with organizations, and state institutions, constant reporting during and after the project will be mandatory.